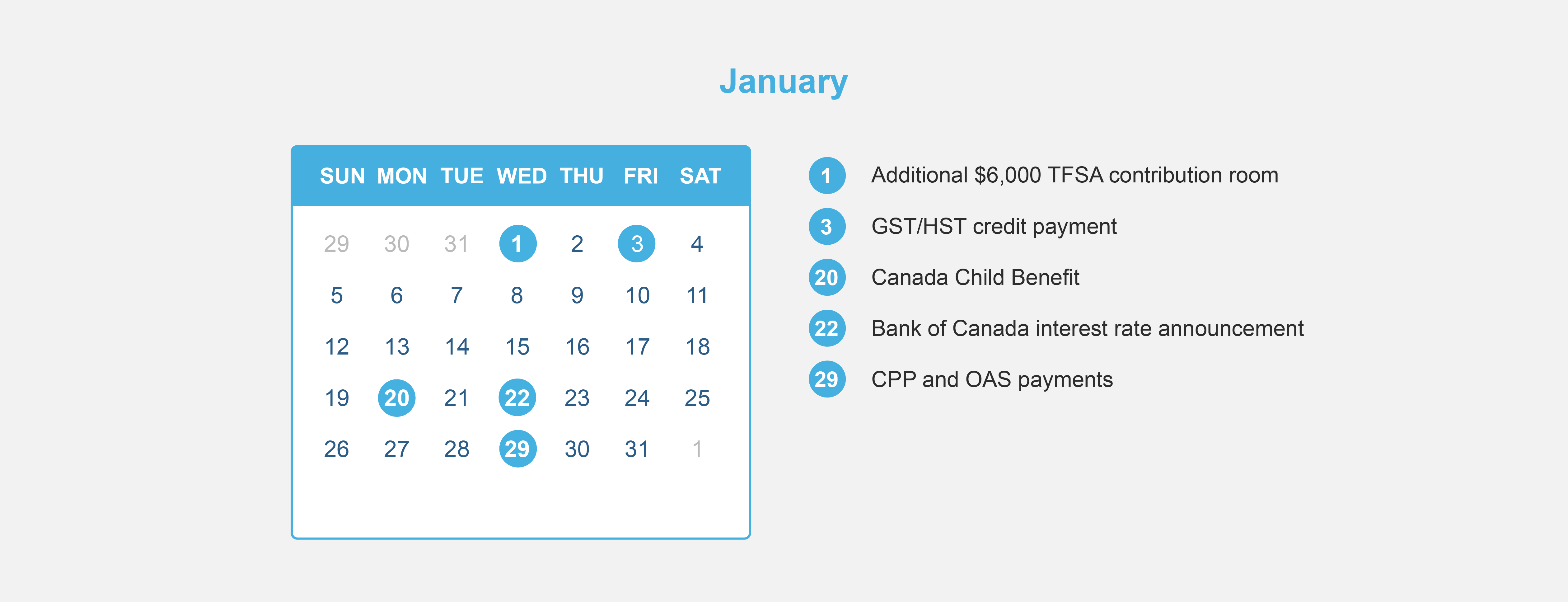
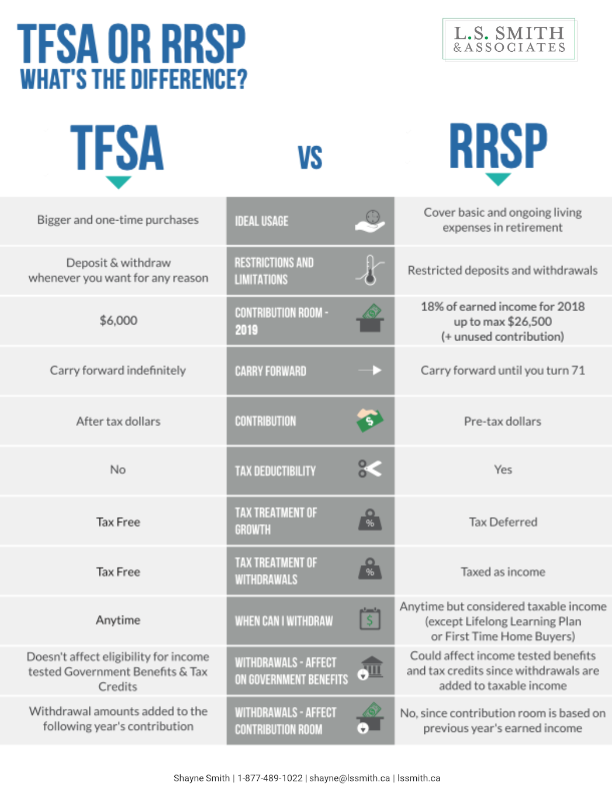
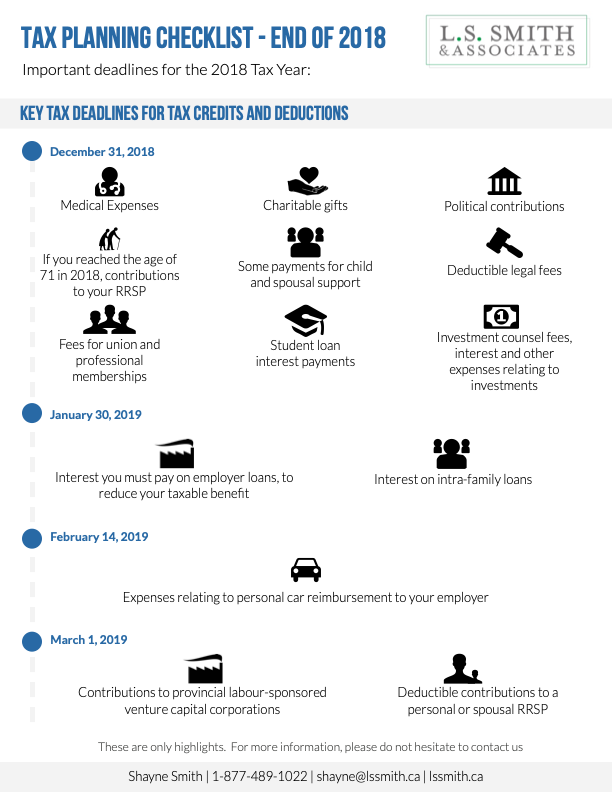
Comparing TFSAs and RRSPs – 2020
If you are seeking ways to save in the most tax-efficient manner available, TFSAs and RRSPs can both be effective options for you to achieve your savings goals more quickly. However, each plan does have distinct differences and advantages / disadvantages. We’ve separated our comparisons into 2 different infographics: deposits and withdrawals.
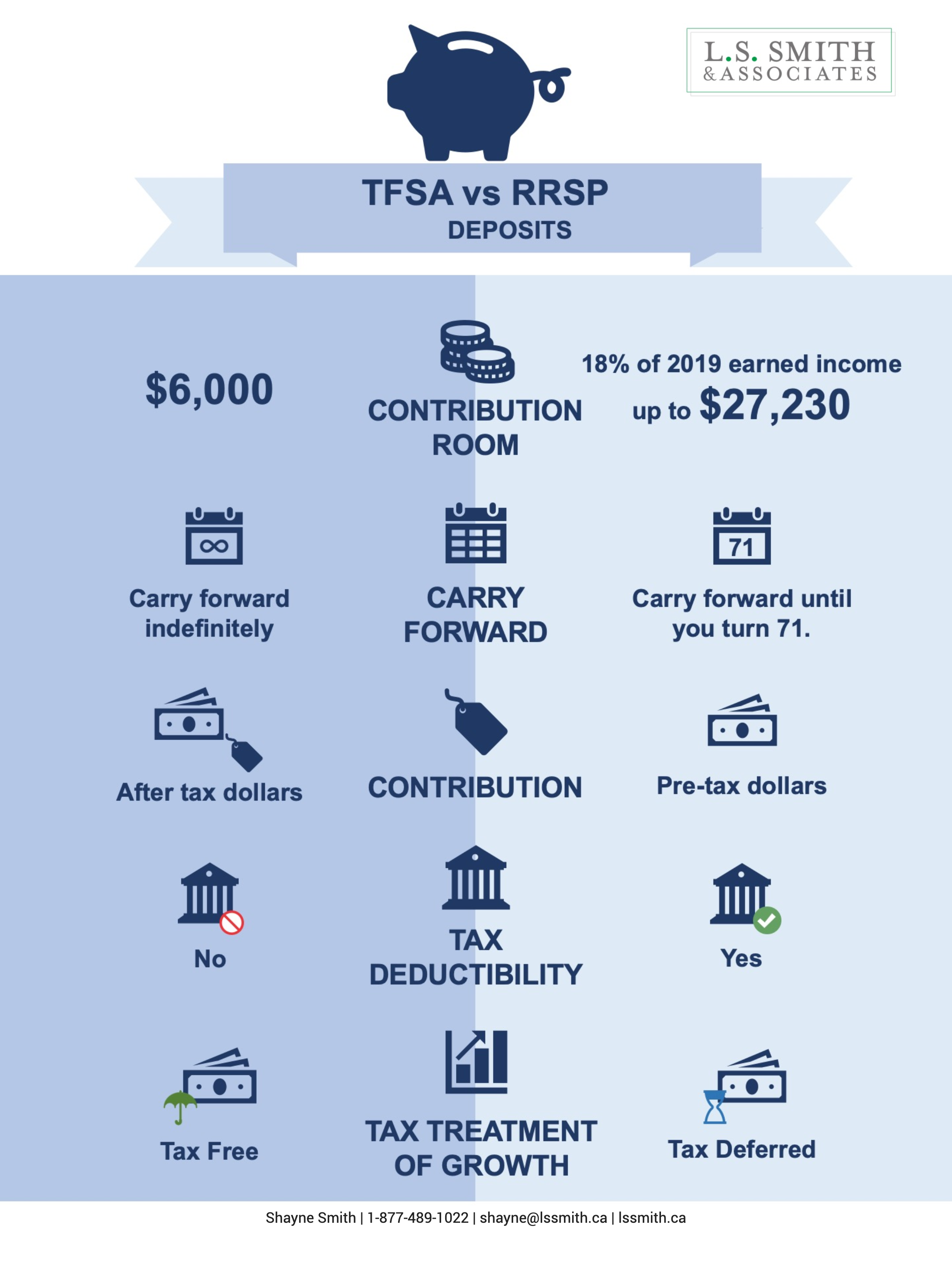
In the Deposit phase, we look at:
-
Contribution Room
-
Carry Forward
-
Contribution
-
Tax Deductibility
-
Tax Treatment of Growth
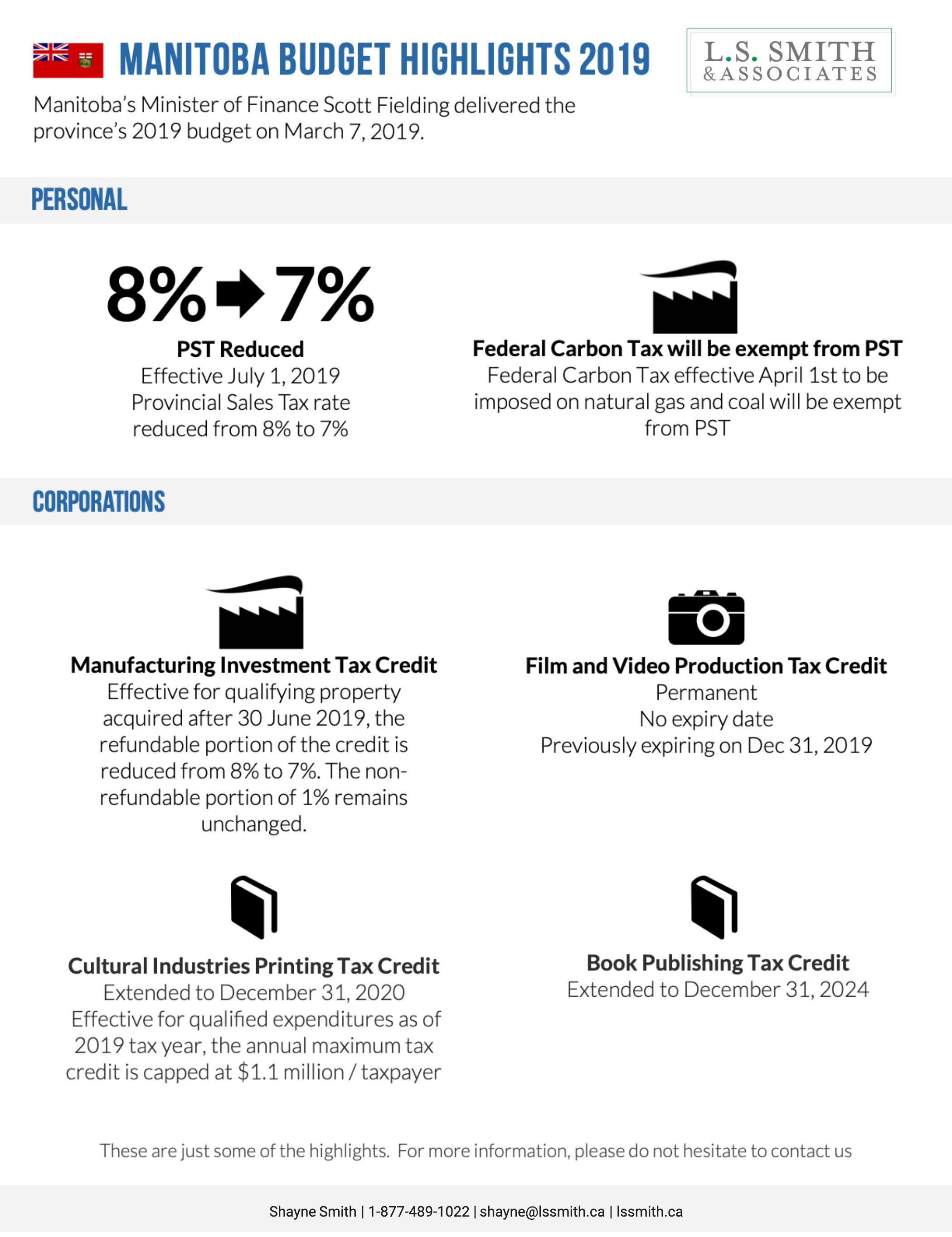
Contribution Room
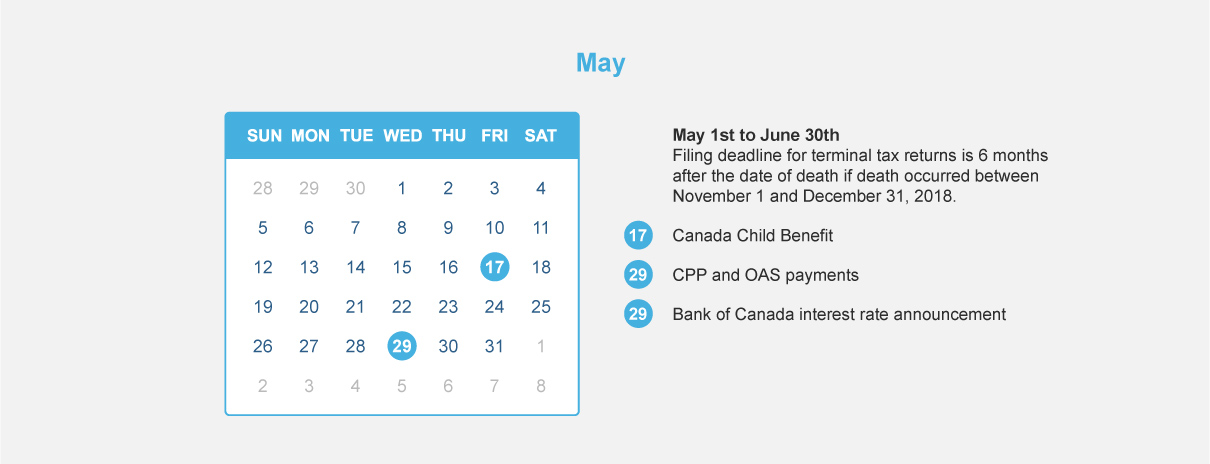
TFSA : $6,000 for 2020. If you never opened a TFSA, you can contribute up to $69,500 today.
-
$5,000 for each year from 2009 to 2012;
-
$5,500 for each of 2013 and 2014;
-
$10,000 for 2015;
-
$5,500 for each of 2016, 2017 and 2019
-
$6,000 for each of 2019 and 2020
RRSP : 18% of your 2020 pre-tax earned income or $27,230. So for example if you earned $60,000, then your deduction limit would be $10,800 (18% x $60,000). If you earned $200,000, then your deduction limit would be capped at the max limit of $27,230.
Carry Forward
TFSA : You can carry forward your unused contribution room indefinitely, as long as your a Canadian resident, older than age 18 with a valid social insurance number. Withdrawals will usually result in new contribution room.
RRSP : You can carry forward your unused contribution room until the age of 71 when you have to convert your RRSP to a RRIF. Any withdrawals made from your RRSP will not result in new contribution room.
Contribution
TFSA : You are contributing to your TFSA with After-tax dollars.
RRSP : You are contributing to your RRSP with Pre-tax dollars.
Tax Deductibility
TFSA : Contributions are not tax deductible.
RRSP : Contributions are tax deductible.
Tax Treatment of Growth
TFSA : The growth inside a TFSA is tax free therefore it’s a great savings vehicle for immediate objectives such as a down payment for a home.
RRSP : The growth inside an RRSP is tax deferred, which means at withdrawal, you will need to pay tax, therefore it’s a good choice for long term goals such as retirement.

In the Withdrawals phase, we look at:
-
Conversion
-
Tax Treatment
-
Government Benefits
-
Contribution Room
Conversion
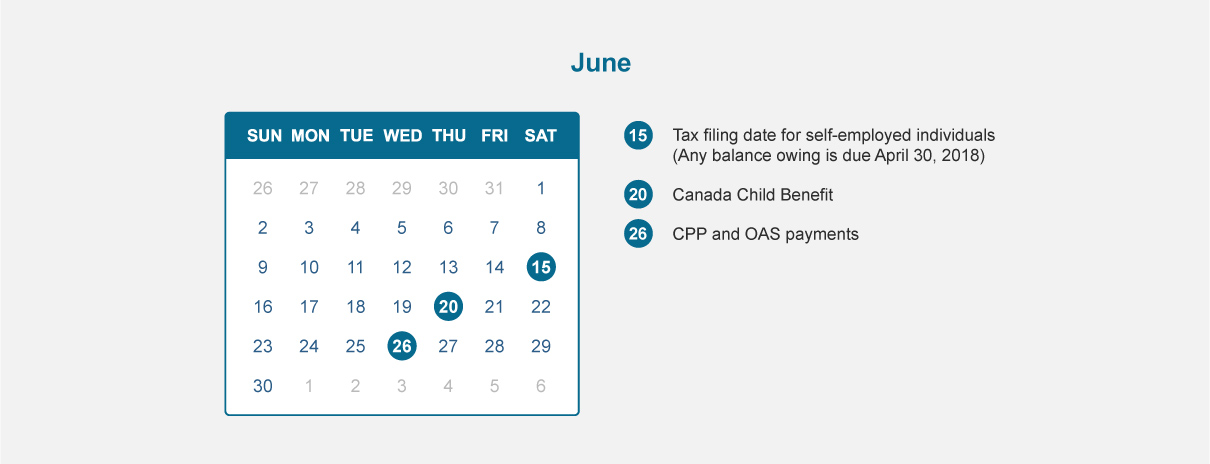
TFSA : With a TFSA, there’s no conversion.
RRSP : You must convert your RRSP to a Registered Retirement Income Fund by December 31st of the year you turn 71.
Tax Treatment
TFSA : You can make tax-free withdrawals.
RRSP : Your withdrawals are taxed as income except for withdrawals under the Home Buyers Plan, which you can withdraw up to $35,000 providing you pay within 15 years or Lifelong Learning Plan, which you can withdraw up to $20,000 ($10,000 per year) providing that the money is paid back within 10 years.
Government Benefits
TFSA : Your withdrawals doesn’t affect eligibility for income tested government benefit because TFSA withdrawals aren’t included as taxable income.
RRSP : RRSP withdrawals are treated as taxable income therefore withdrawals may affect income tested tax credits such as Canada Child Tax Benefit, the Working Income Tax Benefit, the Goods and Services Tax Credit and the Age Credit. Withdrawals may also affect government benefits you receive including Old Age Security, Guaranteed Income Supplement and Employment Insurance benefits.
Contribution Room
TFSA : You can carry forward your unused contribution room indefinitely, as long as your a Canadian resident, older than age 18 with a valid social insurance number. Withdrawals will usually result in new contribution room to the following year’s contribution.
RRSP : Contribution room is based on your previous year’s earned income. You can carry forward your unused contribution room until the age of 71 when you have to convert your RRSP to a RRIF. Any withdrawals made from your RRSP will not result in new contribution room.
An additional different to note is that:
-
You are able to specify your spouse as your beneficiary with both your TFSA and your RRSP, however there is a key difference with how your savings are treated upon your spouse’s death. With an RRSP, there will be taxes payable upon the monies left in the plan by your children who inherit it, whereas with a TFSA, tax is only paid on the increase in the value of the plan since the date of death in the year that it is inherited by your children. What’s more, no tax is payable if the value that they receive is less than the value of the TFSA at the time of death.
In summary, your unique financial needs will provide information on what makes the most sense for you.
Contact us and we can help.