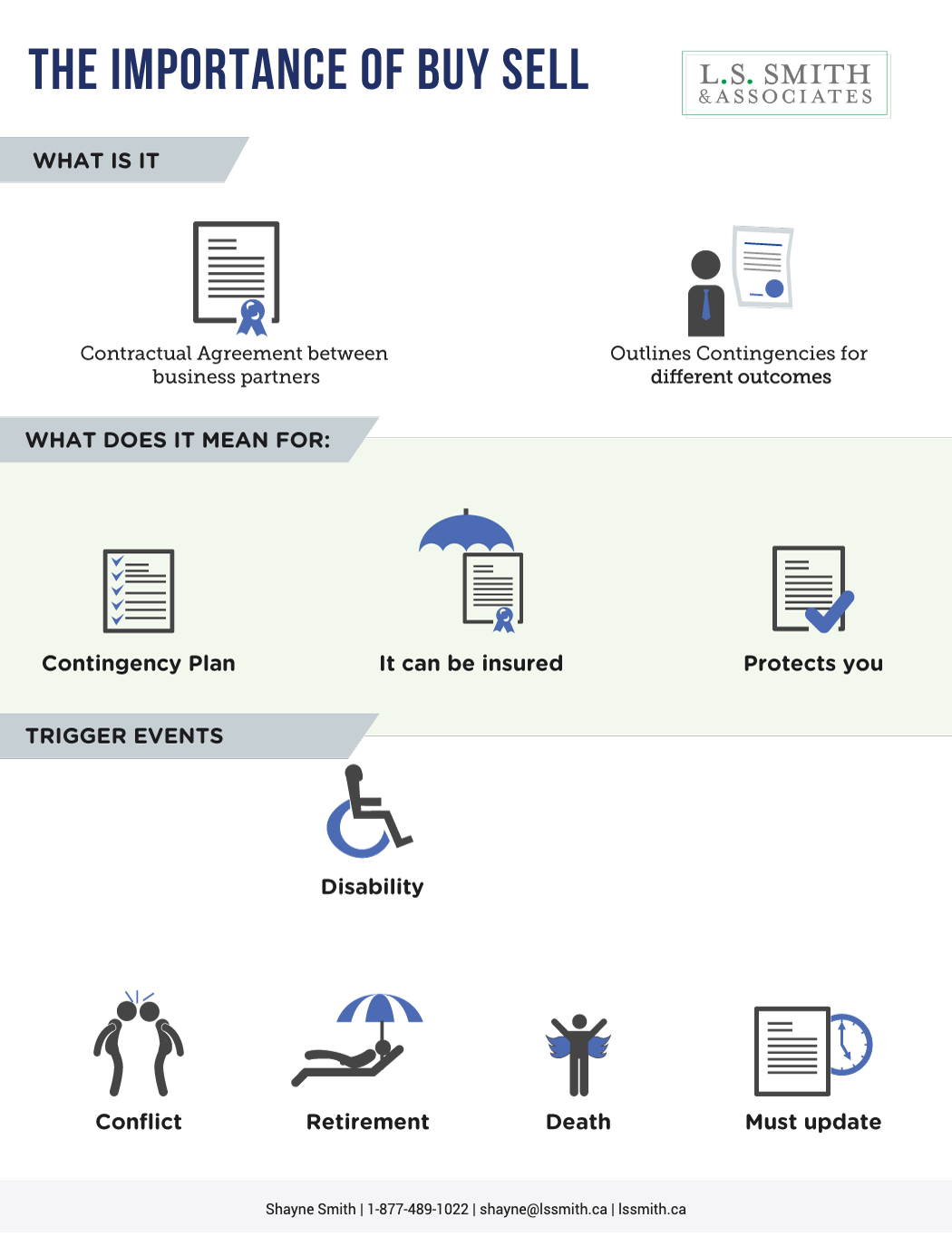
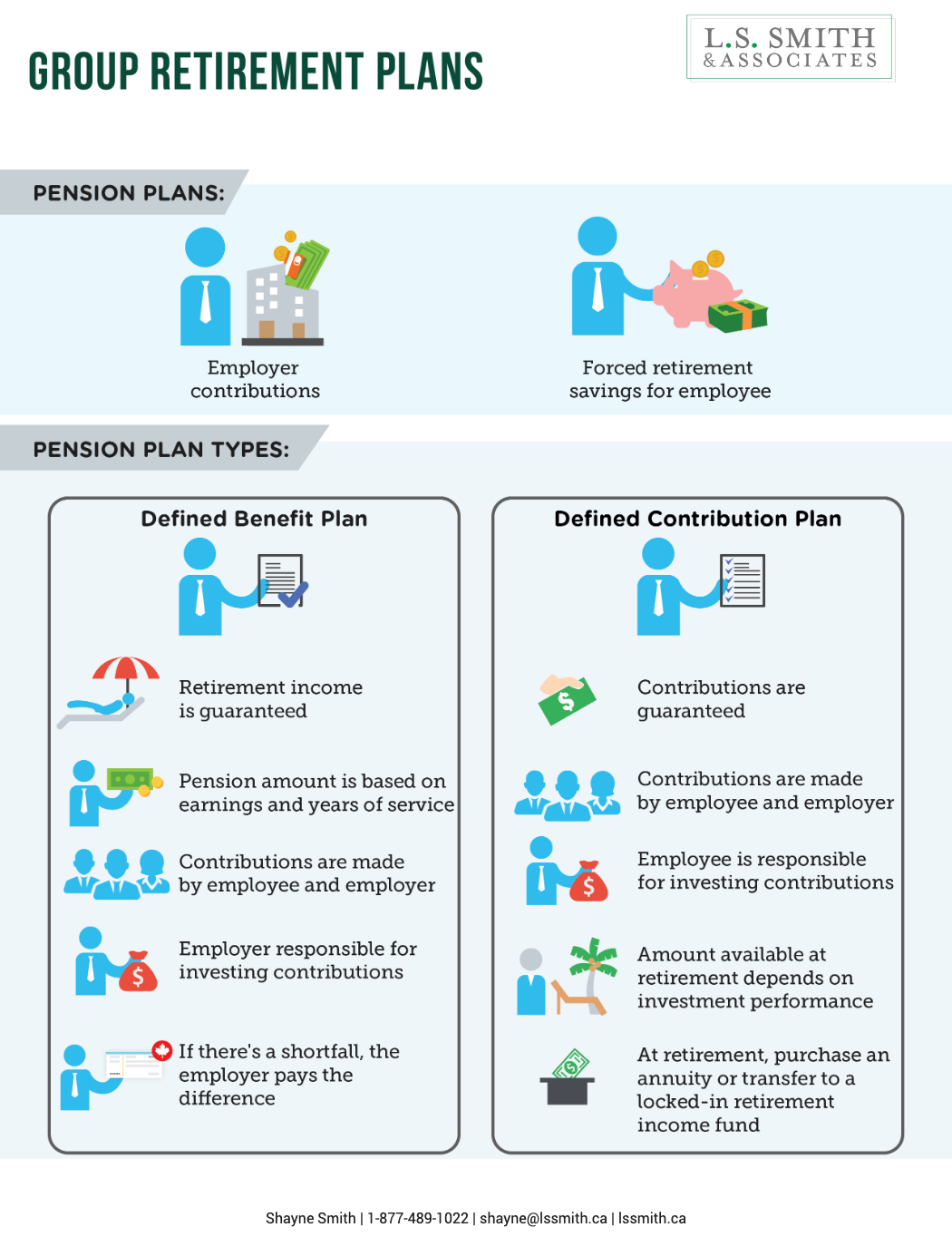
Federal Budget 2023 Highlights
On March 28, 2023, the Federal Government released their 2032 budget. This article highlights the following financial measures:
-
New transfer options associated with Bill C-208 for intergenerational transfer.
-
New rules for employee ownership trusts.
-
Changes to how the Alternative Minimum Tax is calculated.
-
Improvements to Registered Education Savings Plans.
-
Expanding access to Registered Disability Savings Plans.
-
Grocery rebate.
-
Deduction for tradespeople tool expenses.
-
Automatic tax filing.
-
New Canadian Dental Care Plan.
Amendments To Bill C-208 Intergenerational Transfer Introduces Two New Transfer Options
Budget 2023 introduces two transfer options associated with the intergenerational transfer of a business:
-
An immediate intergenerational business transfer (three-year test) based on arm’s length sales terms.
-
A gradual intergenerational business transfer (five-to-ten-year test) based on estate freeze characteristics.
For the three-year test, the parent must transfer both legal and factual control of the business, including an immediate transfer of a majority of voting shares and the balance, within 36 months. The parent must also transfer a majority of the common growth shares within the same time frame. Additionally, the parent must transfer management of the business to their child within a reasonable time, with a 36-month safe harbour. The child or children must retain legal control for 36 months following the share transfer, and at least one child must remain actively involved in the business during this period.
For the gradual transfer option, the conditions are similar to the immediate transfer, but with a few differences. The parent must transfer legal control, including an immediate transfer of a majority of voting shares and the balance, within 36 months. They must also transfer a majority of the common growth shares and the balance of common growth shares within the same time frame. As well, within 10 years of the initial sale, parents must reduce the economic value of their debt and equity interests in the business to 50% of the value of their interest in a farm or fishing corporation at the initial sale time, or 30% of the value of their interest in a small business corporation at the initial sale time. The child or children must retain legal control for the greater of 60 months or until the business transfer is completed, and at least one child must remain actively involved in the business during this period.
The extended intergenerational transfer now applies to children, grandchildren, stepchildren, children-in-law, nieces and nephews and grandnieces and grandnephews.
The changes apply to transactions that occur on or after January 1, 2024. If the election is made, the capital gain reserve period is extended to ten years, and the limitation period for assessing a return is extended to three years for an immediate transfer and ten years for a gradual business transfer.
New Rules for Employee Ownership Trusts
The employees of a business can use an employee ownership trust (EOT) to purchase the business without having to pay the owner directly to acquire shares. Business owners can use an EOT as part of their succession planning.
Budget 2023 introduces new rules for using ownership trusts (EOTs) as follows:
-
Extending the five-year capital gains reserve to ten years for qualifying business transfers to an EOT.
-
A new exception to the current shareholder loan rule which extends the repayment period from one to fifteen years for amounts loaned to the EOT from a qualifying business to purchase shares in a qualifying business transfer.
-
Exempts EOTs from the 21-year deemed disposition rule that applies to some trusts. This means that shares can be held indefinitely for the benefit of employees.
Clean Energy Credits
The upcoming Budget 2023 is set to introduce a series of measures aimed at encouraging the adoption of clean energy. These measures include several business tax incentives such as:
-
Clean Electricity Investment Tax Credit: This is a refundable tax credit of 15% for investments in equipment and activities for generating electricity and transmitting it between provinces. The credit will be available to new and refurbished projects starting from March 28, 2023, and will end in 2034.
-
Clean Technology Manufacturing Credit: This tax credit is worth 30% of the cost of investments in new machinery and equipment for processing or manufacturing clean technologies and critical minerals. It applies to property acquired and put into use after January 1, 2024. The credit will be phased out starting in 2032 and fully eliminated in 2034.
-
Clean Hydrogen Investment Tax Credit: It offers a refundable tax credit ranging from 15% to 40% of eligible project expenses that produce clean hydrogen, as well as a 15% tax credit for certain equipment.
-
Clean Technology Investment Tax Credit: This tax credit will be expanded to include geothermal systems that qualify for capital cost allowance under Classes 43.1 and 43.2. The phase-out will begin in 2034, and it will not be available after that date.
-
Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage Investment Tax Credit (CCUS): The budget broadens and adjusts specific criteria for the refundable Investment Tax Credit (ITC) for CCUS. Qualified equipment now includes dual-purpose machinery that generates heat and/or power or utilizes water for CCUS and an additional process, as long as it meets all other requirements for the credit. The expense of such equipment is eligible on a proportionate basis, based on the anticipated energy or material balance supporting the CCUS process during the project’s initial 20 years.
-
Reduced rates for zero-emission technology manufacturers: The reduced tax rates of 4.5% and 7.5% for zero-emission technology manufacturers will be extended for three years until 2034, with phase-out starting in 2032. The eligibility will expand to include the manufacturing of nuclear energy equipment and processing and recycling of nuclear fuels and heavy water for taxation years starting after 2023.
-
Lithium from brines: Allow producers of lithium from brines to issue flow-through shares and expand the Critical Mineral Exploration Tax Credit’s eligibility to include lithium from brines.
Changes To How Alternative Minimum Tax Is Calculated
Budget 2023 proposed several changes to calculating the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT), including the following:
-
The capital gains inclusion rate will increase from 80 percent to 100 percent, while capital losses and allowable business investment losses will apply at a rate of 50 percent.
-
The inclusion rate for employee stock option benefits will be altered to 100 percent, and for capital gains resulting from the donation of publicly listed securities, it will be modified to 30 percent.
-
The 30 percent inclusion rate will also apply to employee stock option benefits if any deduction is available because underlying shares are also publicly listed securities that were donated.
-
Certain deductions and expenses will now be limited to 50 percent, and only 50 percent of non-refundable credits (excluding a special foreign tax credit) will be permitted to reduce the AMT.
-
The AMT tax rate will increase from 15 percent to 20.5 percent.
-
The AMT exemption will rise from the present allowable deduction of $40,000 for individuals to an amount indexed to the fourth tax bracket, expected to be $173,000 in 2024.
-
The AMT carryforward period will remain unaltered at seven years.
Improving Registered Education Savings Plans (RESPs)
Budget 2023 introduces the following changes to RESPs:
-
As of March 28, 2023, beneficiaries may withdraw Educational Assistance Payments (EAPs) up to $8,000 (from $5,000) for full-time programs and $4,000 (from $2,500) for part-time programs.
-
Individuals who withdrew EAPs before March 28, 2023, may be able to withdraw an additional EAP amount, subject to the new limits and the plan terms.
-
Divorced or separated parents can now open joint RESPs for one or more of their children.
Expanding Access to Registered Disability Savings Plans
Qualifying family members, such as a parent, a spouse, or a common-law partner, can open an RDSP and be the plan holder for an adult with mental disabilities whose ability to enter into an RDSP contract is in doubt and who does not have a legal representative.
Budget 2023 announces the government’s intention to extend the provision that allows this until December 31, 2026. To further increase access to RDSPs, the government also intends to expand the provision to include adult siblings of an RDSP beneficiary.
Grocery Rebate
The Budget 2023 will implement the Grocery Rebate, which will be a one-time payment managed through the Goods and Services Tax Credit (GSTC) system. The maximum amount that can be claimed under the Grocery Rebate is:
-
$153 for each adult
-
$81 for each child
-
$81 for a single supplement.
The implementation of the Grocery Rebate will be gradual and will follow the same income thresholds as the present GSTC regulations.
Deduction for Tradespeople’s Tool Expenses
Budget 2023 increases the employment deduction for tradespeople’s tools to $1,000 from $500. This is effective for 2023 and subsequent taxation years.
Automatic Tax Filing
The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) will pilot a new automatic filing service for Canadians who currently do not file their taxes to help them receive certain benefits to which they are entitled.
The CRA also plans to expand taxpayer eligibility for the File My Return service, which allows taxpayers to file their tax returns by telephone.
Canadian Dental Care Plan
In Budget 2023, the federal government is investing in dental care for Canadians with the new Canadian Dental Care Plan. The plan will provide dental coverage for uninsured Canadians with annual family incomes of less than $90,000, with no co-pays for those under $70,000.
The budget allows the CRA to share taxpayer information for the Canadian Dental Care Plan with an official of Employment and Social Development Canada or Health Canada solely to administer or enforce the plan.
Wondering How This May Impact You?
If you have any questions or concerns about how the new federal budget may impact you, call us – we’d be happy to help you!










-Shayne-Smith-N2cCT9YpXqWbeLbXq.png)