Coronavirus & Market Uncertainty- What you should do.
Over the last week, the financial market has taken a downturn amidst fears over Coronavirus. The S&P 500 had its worst weekly drop since the financial crisis in 2008, after setting all-time highs the prior week.*
Understandably, investors are anxious about their money. If you are concerned with your portfolio, you’re not the only one, however during times of market volatility, it’s important to stay levelheaded to avoid making financial missteps.
Keep Calm
In situations like these, it’s important to keep perspective. This is not the first time the market has taken a downturn, market corrections are a natural part of the investment cycle and over long term, individuals that remain invested can use the volatility as an opportunity to buy will be rewarded.
The media can make it seem like each market downturn is worse than before. In reality though, volatility doesn’t hurt investors but if selling in a downturn, it will lock in losses.
Keep Up-to-Date
Currently, there isn’t enough information to know how the Coronavirus will affect the market, over the short, medium and long term however it’s important to know that the financial market doesn’t like uncertainty. Therefore, as further developments come to light, there will likely be a correction to the market.
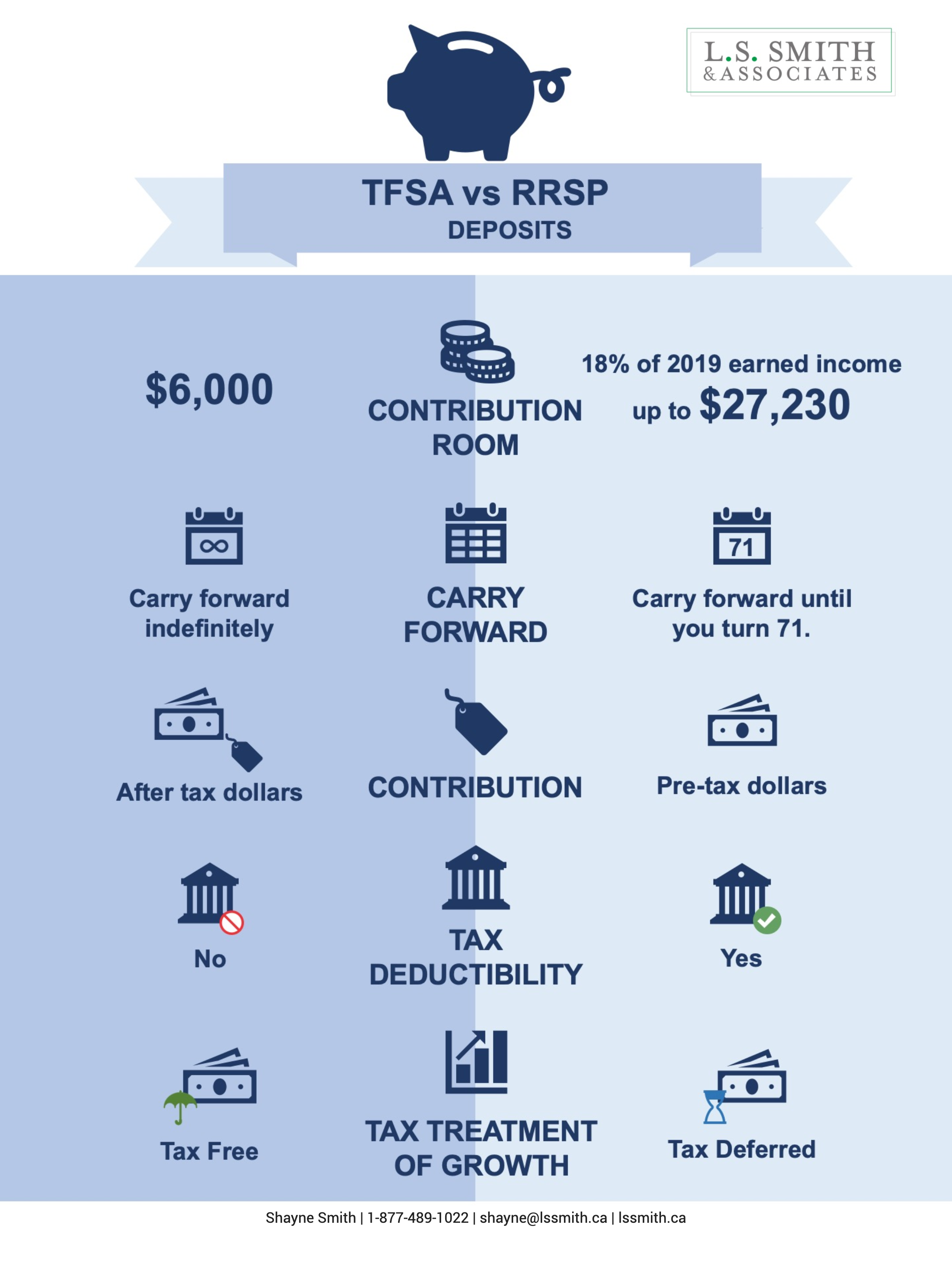
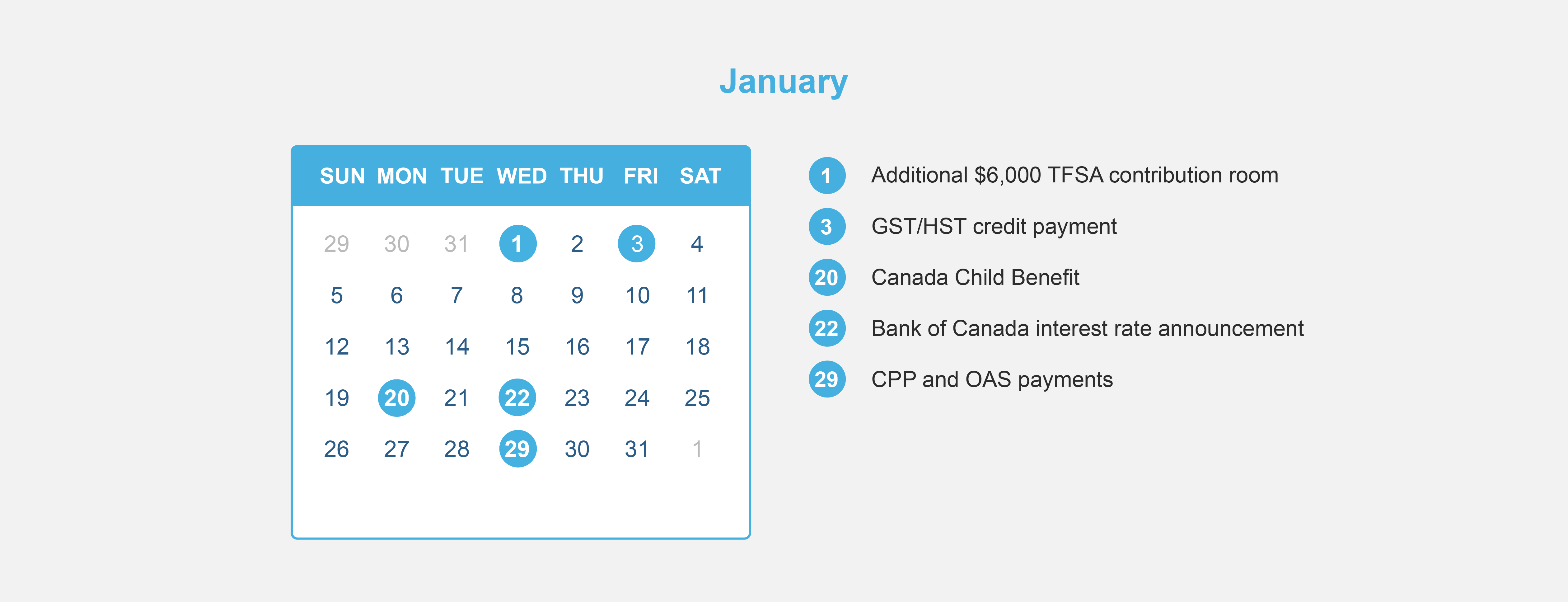
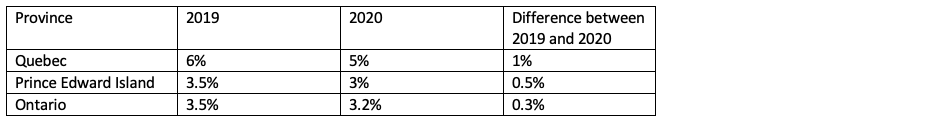
How have markets reacted to virus outbreaks in the past?
The table and chart below, show how the S&P 500 has performed during similar virus outbreaks in the past. While the impact can be negative, the long-term impact has been limited. In all past scenarios markets were higher 12 months after the virus was identified.**
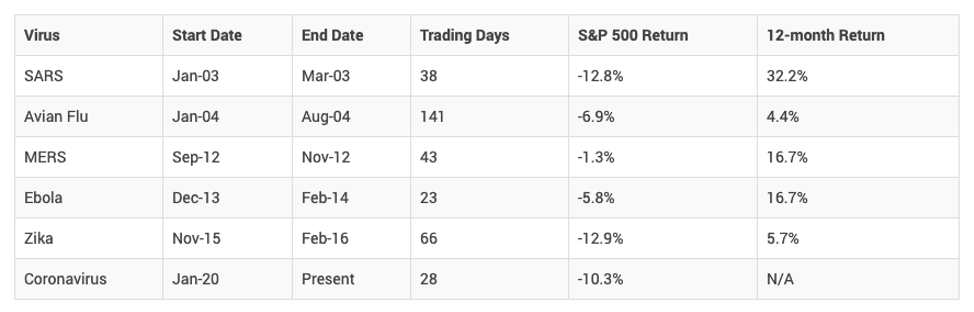
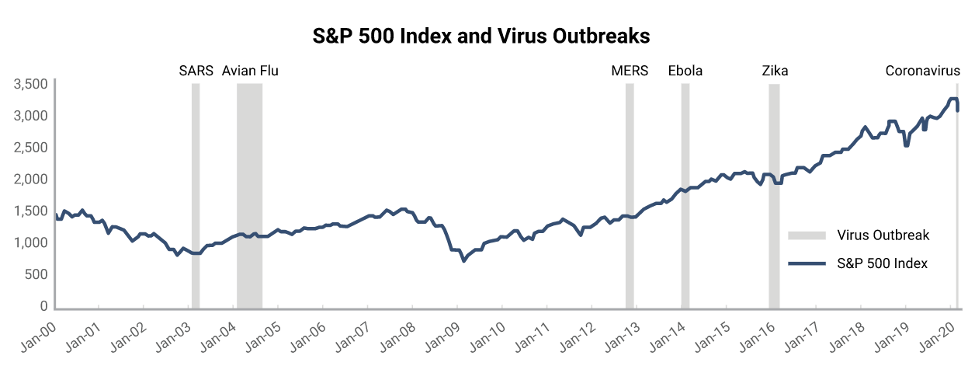
Source: Bloomberg Finance L.P., CitiResearch, FactSet. As at February 27, 2020. The starting date for the 12-month return is
the month each virus was identified.
Keep in mind your portfolio is diversified
We know market downturns can be stressful and being bombarded by media reports doesn’t help but keep in mind your portfolio is diversified It’s important to remember that your portfolio is tailored to your unique investment time horizon, personal situation and financial goals. If you do have questions about your portfolio, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Review your investments
This is a good time to review all your investment accounts including your TFSA, RRSP or RRIF to ensure you are diversified. If you haven’t reviewed the accounts that we don’t manage, please reach out to our office and we can provide you with recommendations that align with your financial goals.
Keep in touch
We’re here for you and hope to serve you by helping you make objective and educated financial decisions. These decisions will help you stay the course so you can achieve your financial goals.
If you have friends or family that need help with their investments, we are happy to offer a complimentary review. We will discuss what their financial goals are and what makes the most sense for their situation. Often by working with a financial advisor, it can help them feel more confident about their finances.
At any time, should you wish to discuss or review your investments, please contact us. We’re here to support you.